DATA CLASSIFICATION: USE CASE – RISK MITIGATION
Classifier system mitigates risk in the field of information management by providing categorization and involving users in data labelling process. As an effect, it makes them partially responsible for the data protection process. Why is it worth classifying data? You can read in the text below.
In previous article, dedicated to data classification, we defined it’s main goal. It is to capture a few percent of the critical data among the organizational „noise” and ensure their visibility.
Below we will cover one of what Gartner identifies as „main areas of use” for file classification systems.
The article can be especially useful in a pre-implementation case to determine to what extent the software can empower your data protection initiative.
In its File Analysis Software (into which classification systems integrate) Market Guide, Gartner lists four major areas of use for this software.
The first is RISK MITIGATION, briefly characterized in the following sections:
- Limits access to information containing Personally Identifiable Information (PII).
- It allows you to control location and access to intellectual property (IP).
- Reduces the attack surface for sensitive data.
- It allows you to add an additional rule execution parameter in other programs, eg DLP.
For the purposes of various requirements analysis, we will discuss the above points and suggest how to apply them.
Limiting access to information containing personal data
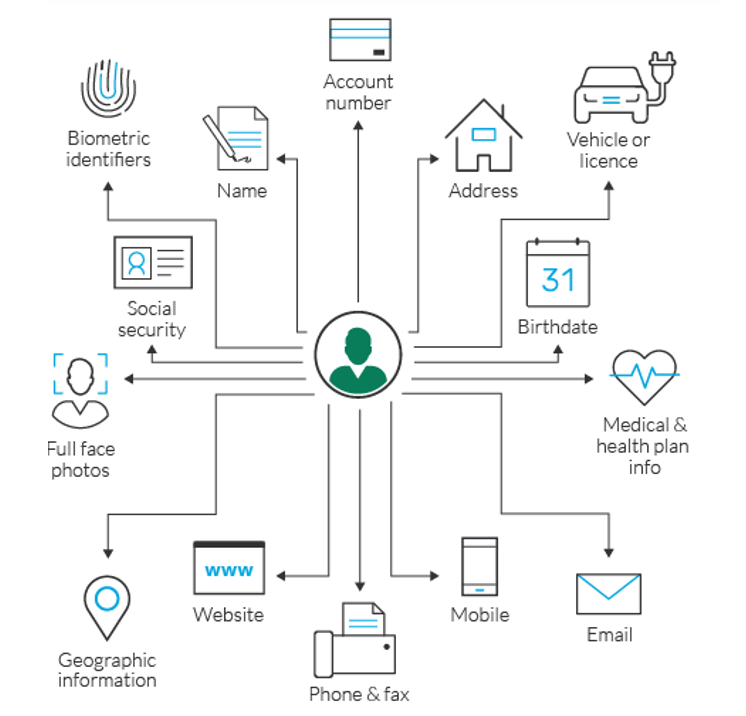
Personal data (PII) is data that can be used to identify, contact or locate a specific person or to distinguish one person from another.
Personally identifiable information is often defined as a person’s first name or initial and surname combined with one or more of the following data elements:
- Social Security Number
- Driver’s license number
- ID card or passport number
- Credit card number
- A financial account number combined with a security code, access code or password that would allow access to the account Medical or health insurance information.
However, when applying classification mechanisms, we tend to rely on a different level of ‘labeling’ – eg ‘Confidential’, ‘Internal’, ‘Public’. If we were to classify every document containing personal data as “confidential” – the number of confidential documents in an organization would quickly exceed any control limits.
Therefore, the key task is to identify in which categories of information (which you will use in your project) the personal data will be and how to take this into account.
- Subjective definition of “groups” of personal data – according to the indicative level of sensitivity.
- The level of confidentiality required by specific groups of personal data.
- The potential impact that a personal data breach or data corruption would have on the individuals involved.
- The importance of the availability of this data.
You may find that some information changes its category just because the file contains personal data.
It is worth mentioning here that leading solutions for data classification allow to establish „subcategories” which define general categories, eg CONFIDENTIAL PERSONAL DATA. Any provisions regarding the categorization of files containing personal data must be reflected in the appropriate security policy.
Watch also:
Location and access control of intellectual property (IP)
Usually it happens through integration with DRM – Digital Rights Management-class system.
The classification systems themselves provide the possibility of conducting the so-called discovery – determining what information (from the categorization) is inside the file, but at a fairly high level of generality. To ensure the possibility of advanced categorization of files based on the content (from the central console) – it is worth considering integration with the DLP system – Data Loss Prevention.
The data classification system improves DLP and DRM activities by allowing them to “see” how the creator has classified a given file (or how the file has automatically classified the program itself).
Reducing the area of attack for sensitive data
Data classification systems support data protection in 3 areas:
- Data inventory – they allow to define where the data from certain categories is located, in what amount and types
- User awareness – users who consciously categorize data automatically handle it more carefully, which improves the overall level of security.
- Data protection – the classifier is a technical extension of organizational information security policies. It allows both to categorize files according to the labels described in procedures, and to trigger appropriate rules in other IT security solutions (more on that in point 4).
Option to add an additional rule execution parameter in other programs
References to the integration of the data classifier with technologies such as:
- Data Loss Prevention
- Digital Rights Management
- Identity & Access Management
- File Encryption
The set of files assigned to a given “label” is seen by each of the above solutions as a “group” on which appropriate security policies can be imposed. It is worth adding that the integration with the above is one of the most important parameters when considering the purchase of a data classification solution.
As we can see from the analysis of the above areas – the data classification system reduces the risk by introducing visibility in terms of information categories and involving users in the information categorization process, which in turn makes them co-responsible for the data protection process.
Firms adopt various risk mitigation measures:
- percentage reduction of unauthorized data storage places,
- the number of incidents concerning individual data categories per month (here, without a classifier, it is difficult to talk about categories at all),
- percentage reduction of false-positives from other solutions, eg DLP, by introducing policies based on data from the classifier.
Interestingly, after the implementation, companies improve in each of them. In the next article, we will discuss the subject of assuring the regulatory compliance.




